Lately, website page speed is becoming an increasingly popular topic, and many website owners are obsessing about the Google PageSpeed Insights scores. There are good reasons behind all this, as data has shown that:
- It affects the bounce rate and user experience.
- It is an important search ranking factor on Google and other search engines.

Website speed optimization can be a very technical and challenging process for most website owners who aren’t skilled programmers or SEO experts. However, there are a few fundamental practices that don’t require too much technical expertise and will take you a long way.
Tools for measuring page speed
There is a variety of tools that can help you measure your website speed performance and they mostly work in a similar way. Some of the most popular are:
All of these tools measure how fast the server responds and how much time it takes for the page to load. In this article, we will focus mainly on Google PageSpeed Insights.
Google page speed explained
Before you actually start improving your website speed, you need to understand what the tests are telling you. Visit the PageSpeed Insights online tool and enter a web page URL in the input. Click on the “Analyze” button and wait for a few seconds for the test to finish.
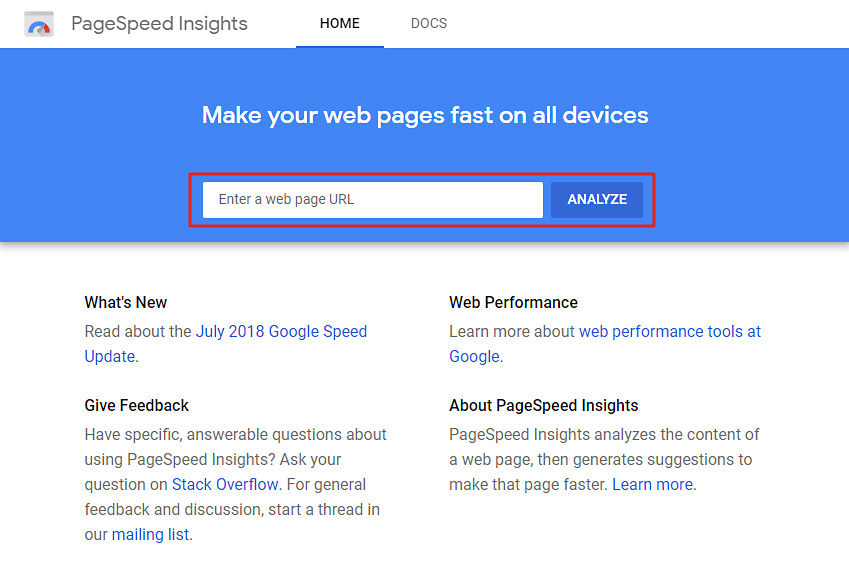
The first section we will focus on is Lab Data, which shows different load times measured by Google on your website. They are not necessarily the actual load times your visitors will experience, as it depends on many factors such as the device they used, their internet connection speed, etc. Nevertheless, they are still good indicators of how your website performs.
Additional note. If Google Chrome has gathered sufficient real-world speed data, the Field Data section will be available as well. This section offers similar data as the Lab Data section, but the results are based on real users instead.
Speed score
At the very top, you will see the speed score, which tells you the overall speed performance of your website. The score is measured separately for mobile and desktop devices.
You should aim for a speed score of at least 60 on mobile devices and 80 on desktop devices. The higher, the better.
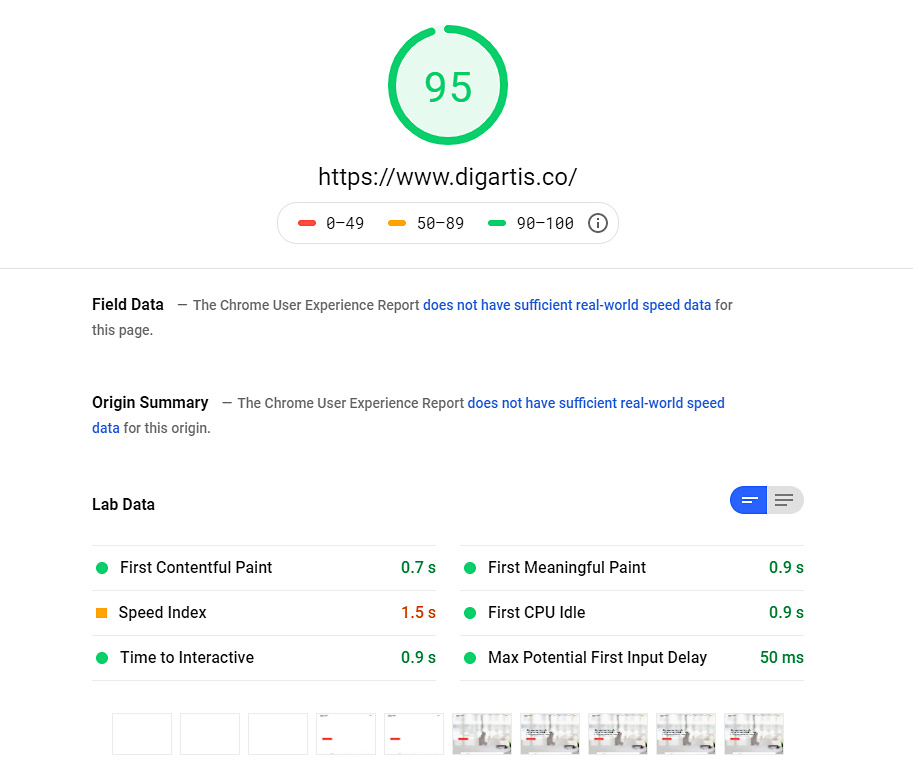
First Meaningful Paint (FMP)
That is arguably the most important indicator of your website speed performance. It tells you how fast the primary content, also known as above-the-fold content, gets loaded and served to the user. Since it’s the first thing a user sees on the website, it must load in the shortest time possible.
Time to Interactive (TTI)
This indicator measures how long it takes for a page to become interactive. In other words, how much time it takes for the page to become fully functional so users can interact with it by clicking buttons, filling out forms, etc.
Common issues and how to fix them
In the Opportunities section, you will find the common issues that are slowing down your website. Fixing them may speed up your website considerably.
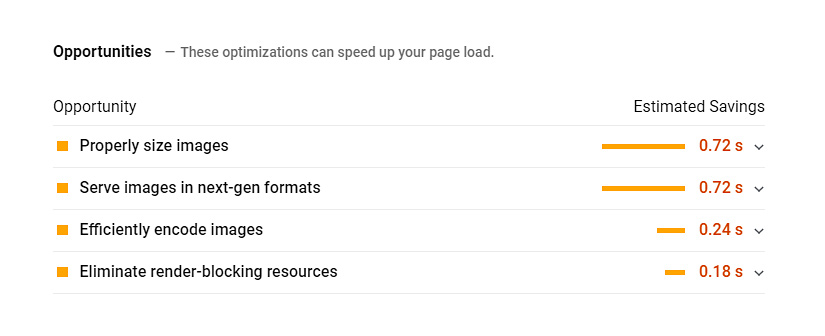
Reduce server response times (TTFB)
When users visit your website, an HTTP request is made to the hosting server. The server responds by sending all the relevant files to their browser so they can see the website.
This indicator tells you how fast your server responds to the request. It will vary depending on how much traffic your server has to handle at the time. It should ideally respond in under 0.2 s. If the response time is much higher (0.6 s or more), you should probably consider switching to a faster hosting option or change your hosting provider.
Other recommendations to reduce server response time:
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN), especially if your website is image or video heavy.
- Use a caching plugin to generate and serve static versions of your web pages. It’ll reduce the number of queries to the database required to serve the content of your web page to the visitor.
- Keep your WordPress software, theme, and plugins updated.
Properly size images
Images are typically the largest files on a website. Therefore, optimizing them and reducing their size might decrease page load times significantly. I have already written about how to optimize images for web in one of our previous blog articles, so I won’t go into details here.
The main idea is to keep images as small as possible without sacrificing too much quality. To achieve that, you should only use the image resolution you actually need. For example, if you only need an image to be 1000px wide on large screens, you should resize it accordingly to save precious kilobytes of data (or twice the size for retina screens). Once properly sized, you should also run your image through an image optimizer software to further reduce its size and optimize it for web delivery.
Eliminate render-blocking resources, Minify CSS and JavaScript and Optimize HTML
This is the most technical part of the website speed optimization process and a common issue that is present on almost any website.
To understand it, you need to know how a web page is built first. A web page is a representation of the HTML file that is sent by the web server to the browser. This file includes references to other external files necessary to fully render the website. These are:
- CSS files that define the styles of the web page. In other words, how the page looks like.
- JavaScript files. They make the website interactive.
- Images and other media files.
For each of these files, a new request is made the first time you visit a web page. If these files are unnecessary large or block the content from being rendered on the screen, it will take longer for the page to load. Furthermore, the more resources the HTML file is requesting, the longer it takes to load. A common practice to mitigate this issue is to combine multiple CSS stylesheets or JavaScript files into one.
If you have a developer, they should solve this for you. If you DIY, you should use a plugin like WP Fastest Cache for this purpose (read below).
Enable text compression
Similar to the issue above, you need some technical know-how to fix it. In a nutshell, text compression means all files are compressed before they are sent to the user’s browser to reduce their size. Enabling this server feature will drastically speed up the site.
You can enable this feature by:
- changing the server configuration .htaccess file, or
- using a plugin like WP Fastest Cache.
We will only talk about the second method as it is much safer and does not require the technical skills needed for server configuration.
Speed up your website with WP Fastest Cache plugin
The WP Fastest Cache plugin has a free version, which will help you quickly fix some of the common issues that are slowing down your website.
First, install and activate the plugin and then navigate to WP Fastest Cache > Settings. You will find many features here to improve your site speed. For a basic setup, you should check the following options:
- Cache system (enables website caching),
- Preload (caches pages/posts automatically to improve future loads),
- New Post (updates cache every time you publish a new post/page),
- Update Post (updates cache every time you update an existing post/page),
- Minify HTML (reduces the size of HTML files),
- Minify CSS (reduces the size of all CSS files),
- Combine CSS (combines all CSS files into one for fewer HTTP requests),
- Combine JS (combines all JS files into one for fewer HTTP requests),
- Gzip (reduces the size of all files sent from server to visitors browser),
- Browser caching (enables browser caching for faster load).
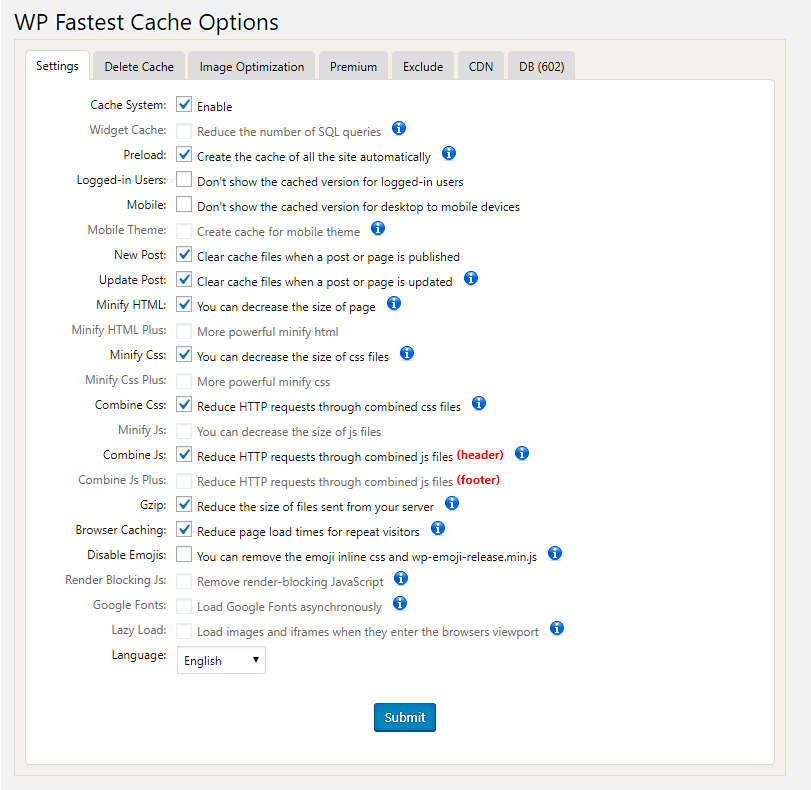
Premium users can enable additional features such as Minify HTML Plus, Minify CSS Plus, Minify JS, Combine JS Plus, and Render Blocking JS. These will help you further decrease load times. The premium version also offers batch optimization of images.
When done with the settings, go to the Delete Cache tab and click on the Delete Cache button. Your website should be loading much quicker now!
Conclusion
Website speed optimization can be a very tedious and technically demanding process, but a very important one nonetheless. As Google and other search engines are adding more weight to page speed in their ranking algorithms, improving it is no longer optional but rather necessary if you’re serious about SEO. We hope this article gives you a sound understanding of how page speed gets calculated and what factors affect it, so you can deal with it effectively.
Has this article helped you increase your page speed? Please let us know in the comments below.



